Use the following powershell script to find the last users to login to a box since a given date, in this case the 21st April 2022 at 12pm until midnight on the 22nd April 2022 :-
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{logname='Security'; id=4624; StartTime="2022-04-21 12:00"; EndTime="2022-04-22 00:00"} -MaxEvents 5000 | Where-Object {($_.Message -like '*Logon Type: 10*')} | select -Property @{Name = 'Info'; Expression = {$_.Message.SubString($_.Message.LastIndexOf("Network Account Name:") -195,300)}},Id, TimeCreated, Message -First 10 | fl Id, TimeCreated, Info
Further to this, to find all the times a particular user has logged on to a machine, use the following query
Get-WinEvent -LogName 'Security' -FilterXPath 'Event[System[EventID=4624] and EventData[Data[@Name="TargetUserName"]="justusernamenodomain"]]' -MaxEvents 10 | fl id, timecreated
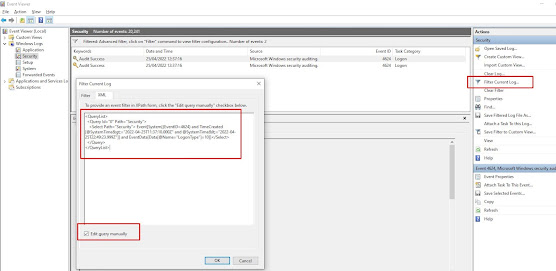
Alternatively you can edit the custom filter in the event log to look like this
<QueryList>
<Query Id="0" Path="Security">
<Select Path="Security">*[System[(EventID=4624) and TimeCreated[@SystemTime>='2022-04-25T15:30:20.000Z' and @SystemTime<='2022-04-25T16:30:20.999Z']]]
and *[EventData[Data[@Name="LogonType"]=10]]
</Select>
</Query>
</QueryList>